In this post, I explained the CSS margin, padding, border, and box model. Also, I tried to clear the common confusion and demonstrate how these three components work together.
Let’s get started.
The easiest-to-understand diagram (box model)
margin
border
padding

/*DESKTOP*/
img {
margin: 90px;
border: 30px solid #222222;
padding: 60px;
}
/*MOBILE*/
img {
margin: 30px;
border: 10px solid #222222;
padding: 20px;
}In this example, the image is the content that has a 90px margin, 30px border, and 60px padding.
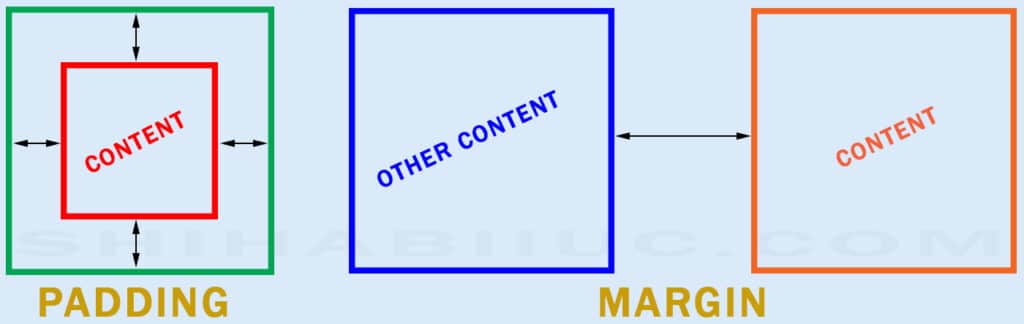
What is the difference between padding and margin?
Padding and margin both create spaces surrounding the content. But what makes them different?
The padding creates space inside the content. And margin creates space outside of the content.
And border lives in between the padding & margin.
CSS Margins
The margin creates space outside of the content.
And CSS margins can share space with their neighbors (if needed or applicable). To demonstrate this behavior of CSS margins, I created 2 divs below.
The first div (yellow), has a 60px margin at the bottom.
And the second div (green), has a 60px margin at the top.
So the total gap between these two divs (yellow & green) should be 120px because 60px + 60px = 120px. But in reality, it’s not the case. And these two divs shared the 60px space among each other.
That means the green (2nd) div shared 60px space from the yellow (1st) div’s bottom margin.
And the opposite is also true. That means the yellow (1st) div shared space from the green (2nd) div’s top margin.
The gap you see between these two divs (yellow & green) is only 60px and not 120px.
1 MISCONCEPTION ABOUT CSS MARGINS AND BOX MODEL
CSS margins do not affect the size of the content.
CSS margins do not affect the size of the content. Though the margin creates space outside of the content, there is a catch.
If the margin runs out of available space on the container, it (content) will exceed the viewport or container.
For example- you have a container that has a 600px width and it contains an image that is also 600px wide.
Now if you assign a 60px margin on the image, it will exceed or go outside of the container. Because there is no available space left for these 60px margins.
But if you assign a 60px padding instead of margins, the image will not go outside of the container. Rather the image will become smaller to hold the 60px padding. And it’s also applicable to borders. The padding and the border behave the same in the CSS box model.
CSS borders
CSS border applies inside the content. That means the more border you add to content will become smaller.

In this example- you have an image with a 200px width and 200px height. Now if you add a 50px border to the image, it (image) will become 50px smaller from all 4 directions.
img {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 50px solid #F70FE8;
}In the above picture, it has a 200px width & height. And I added a 50px pink border to the image. By adding the border, the image became 150px in actual size (width & height). That means the border deducts space from the actual content.
CSS padding
The padding applies to the inside of the content (like the border). If you assign both padding & border to the content, then padding comes first and then border.
Paddings also have an effect on the content size (just like the border).
The actual content becomes smaller after you add padding.

img {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
padding: 30px;
border: 50px solid #EA4335;
}In this example- this is the same 200px image (width & height). But in this case, I added 30px padding (blue area) and the same 50px border (red area).
Now do you see the difference from the above (previous) example?
Since I added 30px padding and 50px border to the image, so it became (30+50) = 80px smaller from all 4 directions.
If you’re wondering what is the actual size of the image at this point! It’s very simple-
width= 200px – (80px × 2) = 40px
height= 200px – (80px × 2) = 40px
That means the actual size is 40px × 40px (after adding 30px padding and 50px border).
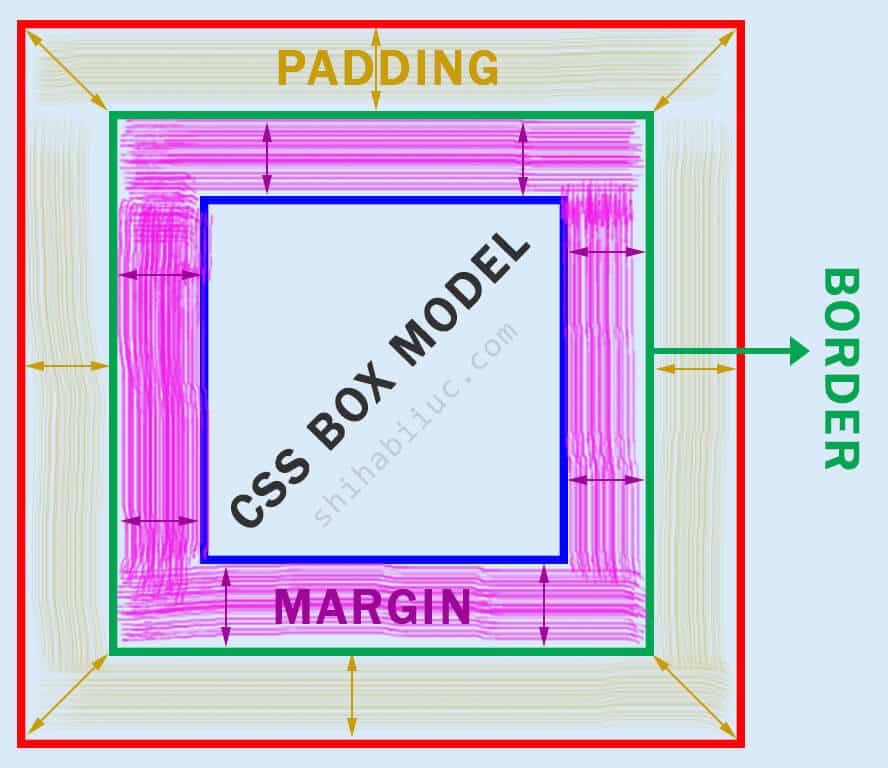
What are the differences among padding, margin & border?
The following picture (CSS box model) clearly shows the difference among padding, margin & border.
In the CSS box model, the blue box refers to the actual content that has margin, border & padding accordingly.
The pink area is the margin, the green rectangle is the actual border and the bread color area refers to the padding.
| Learn & practice CSS with real-world examples |
|---|
| Learn basic CSS from the ground up. |
| Build real projects in HTML CSS. |
Build HTML CSS projects
I hope it has cleared all your confusion about CSS margins vs padding, and also borders. Therefore, if you still have any questions, let me know if I can update the post with new information that has not been pointed out yet.


